Are you considering trying vegan nutrition for ethical, environmental, or health reasons? How to do it, what are the benefits, and what should you pay attention to?
What is vegan nutrition?
Veganism is more than just a diet; it is a lifestyle and philosophy. The essence is to remove the use of animals from human life as much as possible. This includes food, clothing, cosmetics, and other areas. Animal-derived resources are replaced with plant-based, planet-friendly alternatives that align with this philosophy.
Once considered niche and concerning due to a lack of scientific research, vegan nutrition is now one of the most popular dietary styles globally, followed by about 80 million people. It is proven to protect the health of humans, animals, and the planet.
Benefits of vegan nutrition:
Plant-based diets have a significantly lower environmental impact than animal-based nutrition. This is because animal products have high carbon and water footprints due to their production, distribution, storage, and cooking methods. Large-scale animal farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which cause climate change.
If consumed seasonally, locally, and organically, plant-based foods leave a minimal environmental footprint. For instance, while lamb has a carbon footprint of 39.2 kg, lentils leave only 0.9 kg. In short, vegan nutrition prevents animal cruelty and protects living beings while significantly reducing individual footprints.
New research shows that if a diet avoids processed foods, refined oils, and sugars, includes sufficient macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, fats), and is rich in fruits, vegetables, and seeds, transitioning to vegan nutrition can improve physical and mental health. This is achieved by reducing inflammation associated with many diseases, improving gut health with a high-fibre diet, and lowering obesity risks.
How do you adopt vegan nutrition?
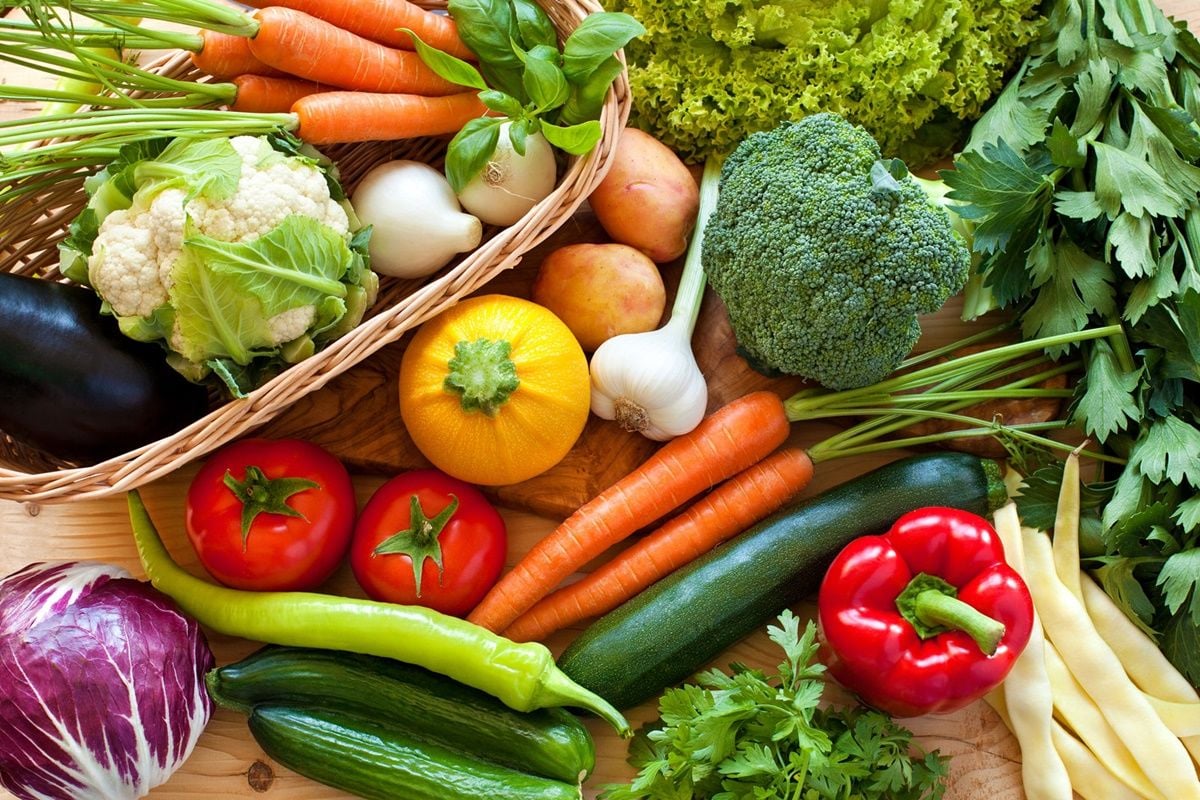
The primary rule of vegan nutrition is eliminating all animal products from your diet. This includes red and white meat, fish, shellfish, eggs, dairy products, and honey. While these are rich in protein, adjusting your body to this new regimen requires attention to certain aspects.
Legumes are your best friends!
The protein gap left by removing animal products is primarily filled with legumes in vegan nutrition. These are excellent plant-based protein sources and rich in essential vitamins and minerals such as iron and calcium. They are nutritious, filling, and the best meat substitutes. Long shelf lives, affordability, minimal plastic packaging, and environmental friendliness make them a sustainable choice.
Pay special attention to Iron and B12:
Iron and B12 are crucial for overall health and are primarily found in animal products. Dark leafy greens, red beets, seeds, nuts, and legumes are rich in iron in vegan diets. Nutritional yeast is a popular source of B12 for vegans. Ensure to consume these foods adequately, monitor levels regularly, and, if necessary, consider supplementation under professional guidance.
Spice it up: Use spices and sauces:
One common concern among those considering vegan diets is that meals may seem bland like they need to be more varied and exciting. However, this is not due to the absence of animal products but rather a lack of spices, sauces, and creativity. Enhancing the flavour of vegan dishes is as simple and affordable as experimenting with rich spices and homemade sauces.